|
| Links |
We parsed the following live from the Web into this page. Such content is managed by its original site and not cached on Discover Life. Please send feedback and corrections directly to the source. See original regarding copyrights and terms of use.
- Australian Faunal Directory
- FishBase
|
|
español |
|
|
Overview |
Main identification features
- head wide, with large paddles
- mouth at front
Head projecting with a pari of paddle-like extensions; large triangular "wings" (pectoral fin flaps); tail long and whip-like; disc above and below covered with small denticles; mouth at front of head, relatively wide; head relatively wide; teeth in lower jaw only; tail without spines .
Dark grey to black above, sometimes with white patches on shoulders; white on underside.
Size: to at least 8 m disc width and over two tons in weight.
Habitat: inshore and offshore pelagic.
Depth: 0-30 m.
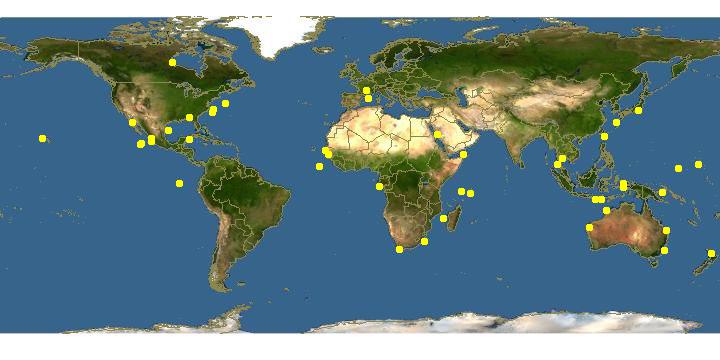
Circumtropical; throughout our region except the northern Gulf of California.
Attributes
Abundance: Common.
Cites: Not listed.
Climate Zone: Northern Subtropical (Cortez Province + Sinaloan Gap); Northern Tropical (Mexican Province to Nicaragua + Revillagigedos); Equatorial (Costa Rica to Ecuador + Galapagos, Clipperton, Cocos, Malpelo).
Depth Range Max: 30 m.
Depth Range Min: 0 m.
Diet: zooplankton; Pelagic crustacea; bony fishes; pelagic fish eggs.
Eastern Pacific Range: Northern limit=35; Southern limit=-4; Western limit=-120; Eastern limit=-78; Latitudinal range=39; Longitudinal range=42.
Egg Type: Live birth; No pelagic larva.
Feeding Group: Planktivore.
FishBase Habitat: Pelagic.
Global Endemism: Circumtropical ( Indian + Pacific + Atlantic Oceans); East Pacific + Atlantic (East +/or West); Transisthmian (East Pacific + Atlantic of Central America); East Pacific + all Atlantic (East+West); All Pacific (West + Central + East); TEP non-endemic; "Transpacific" (East + Central &/or West Pacific); All species.
Habitat: Reef associated (reef + edges-water column & soft bottom); Water column; Estuary.
Inshore Offshore: Inshore; Offshore; In & Offshore.
IUCN Red List: Data deficient; Listed.
Length Max: 800 cm.
Regional Endemism: Island (s); Continent; Continent + Island (s); Eastern Pacific non-endemic; Tropical Eastern Pacific (TEP) non-endemic; All species.
Residency: Resident.
Salinity: Brackish; Marine.
Water Column Position: Near Surface; Surface; Water column only;
|
|
|
Names | |
|
|
|
Links to other sites | |
|
|
|
References |
- Acero , A. and Franke, R., 1995., Nuevos registros de peces cartilaginosos del Parque Nacional Natural Gorgona (Pacifico Colombiano), II. Rayas y Descripcion de una Nueva Especie., Bibl. J. J. Triana, 11:9-21.
- Acero, A. and Franke, R., 2001., Peces del parque nacional natural Gorgona. En: Barrios, L. M. y M. Lopéz-Victoria (Eds.). Gorgona marina: Contribución al conocimiento de una isla única., INVEMAR, Serie Publicaciones Especiales No. 7:123-131.
- Allen , G.R. and Robertson, D.R., 1994., Fishes of the Tropical Eastern Pacific., Crawford House Press Pty Ltd:1-332.
- Béarez, P., 1996., Lista de los Peces Marinos del Ecuador Continental., Revista de Biologia Tropical, 44:731-741.
- Castro-Aguirre, J.L. and Balart, E.F., 2002., La ictiofauna de las islas Revillagigedos y sus relaciones zoogeograficas, con comentarios acerca de su origen y evolucion. En: Lozano-Vilano, M. L. (Ed.). Libro Jubilar en Honor al Dr. Salvador Contreras Balderas., Universidad Autonoma de Nuevo León:153-170.
- Compagno, L.J.V., 1999., Checklist of living elasmobranchs. In Hamlett W.C. (ed.) Sharks, skates, and rays: the biology of elasmobranch fishes., The John Hopkins University Press:471-498.
- Eschmeyer , W. N. , Herald , E. S. and Hamman, H., 1983., A field guide to Pacific coast fishes of North America from the Gulf of Alaska to Baja California. Peterson Field Guide Ser. 28., Houghton Mifflin:336pp.
- Findley, L.T., Hendrickx, M.E., Brusca, R.C., van der Heiden, A.M., Hastings, P.A., Torre, J., 2003., Diversidad de la Macrofauna Marina del Golfo de California, Mexico., CD-ROM versión 1.0. Projecto de la Macrofauna del Golfo . Derechos reservados de los autores y Conservación Internacional.
- Fischer , W. , Krup , F. , Schneider , W. , Sommer , C. , Carpenter , K. E. and Niem, V. H., 1995., Guia FAO para la Identificacion de Especies de para los fines de la Pesca. Pacifico Centro-Oriental. Volumen II. Vertebrados - Parte 1., FAO2:647-1200.
- Galván-Magaña, F., Gutiérrez-Sánchez, F., Abitia-Cárdenas, L.A., Rodríguez-Romero, J., 2000., The distribution and affinities of the shore fishes of the Baja California Sur lagoons. In Aquatic Ecosystems of Mexico: Status and Scope. Eds. M. Manuwar, S.G. Lawrence, I.F. Manuwar & D.F. Malley. Ecovision World Monograph Series., Backhuys Publishers:383-398.
- Gotshall, D.W., 1996., Fishes of Rocas Alijos. In Rocas Alijos. Ed. R. W. Schmieder. Cornell Expeditions., Kluwer Academic Publishers: 347-354.
- Jimenez-Prado, P., Béarez, P., 2004., Peces marinos del Ecuador continental / Marine fishes of continental Ecuador., SIMBIOE/NAZCA/IFEA tomo 1 y 2.
- Jordan , D.S. and Evermann, B.W., 1896., The fishes of North and Middle America: a descriptive catalogue of the species of fish-like vertebrates found in the waters of North America, north of the Isthmus of Panama. Part I., Bull. U.S. Nat. Mus., 47:1-1240.
- Jordan, D.S., 1895., The fishes of Sinaloa., Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences (Series 2), 5:377-514.
- Lopez , M. I. and Bussing, W. A., 1982., Lista provisional de los peces marinos de la Costa Rica., Revista de Biologia Tropical, 30(1):5-26.
- Love, M.S., Mecklenburg, C.W., Mecklenburg, T.A., Thorsteinson, L.K., 2005., es of the West Coast and Alaska: a checklist of North Pacific and Artic Ocena species from Baja California to the Alaska-Yukon border., U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, Biological Resources Division, 288pp.
- Meek , S.E. and Hildebrand, S.F., 1923., The marine fishes of Panama. Part I., Field Mus. Nat. Hist., Zool. Ser. Publ., XV:1-330.
- Ramírez Rodríguez, M., 1997., Producción pesquera en la Bahía de La Paz, B.C.S.. En Urbán Ramírez, J. y M. Ramírez Rodríguez (Eds.). La Bahía de La Paz investigación y conservación., Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur:273-282.
- Rubio, E.A., 1986., Notas sobre la ictiofauna de la Isla de Gorgona, Colombia., Boletin Ecotropica. Univ. Bog. Jorge Tadeo Lozano, 13:86-112.
- Rubio, E.A., 1988., Estudio taxonomico de la ictiofauna acompañante del camaron en areas costeras del Pacifico de Colombia., Memorias del VI Seminario Nacional de las Ciencias del Mar. Comisión Colombiana de Oceanografía. Bogota, Colombia., :169-183.
- Snodgrass , R. E. and Heller, E., 1905., Papers from the Hopkins Stanford Galapagos expedition, 1898-1899. XVII. Shorefishes of the Revillagigedo, Clipperton, Cocos and Galapagos Island., Proc. Wash. Acad. Sci., 6:333-427.
- Sánchez Ortíz , C. , Arreola Robles , J. L. , Aburto Oropeza , O. and Cortés Hernández, M., 1997., Peces de arrecife en la región de La Paz, B.C.S.. En Urbán Ramírez, J. y M. Ramírez Rodríguez (Eds.). La Bahía de La Paz investigación y conservación., Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur:189-200.
- Van der Heiden , A. M. and Findley, L. T., 1988., Lista de los peces marinos del sur de Sinaloa, México., Anales del Centro de Ciencias del Mar y Limnologia de la Universidad Autonoma Nacional de Mexico, 15:209-224.
- Villareal-Cavazos, A., Reyes-Bonilla, H., Bermúdez-Almada, B. and Arizpe-Covarrubias, O., 2000., Los peces del arrecife de Cabo Pulmo, Golfo de California, México: Lista sistemática y aspectos de abundancia y biogeografía., Rev. Biol. Trop., 48:413-424.
- Walbaum, J. J., 1792., Petri Artedi Sueci Genera piscium. In quibus systema totum ichthyologiae proponitur cum classibus, ordinibus, generum characteribus, specierum differentiis, observationibus plurimis. Redactis speciebus 242 ad genera 52. Ichthyologiae, pars iii., Artedi Piscium, (Pt. 3):1-723.
- Walker, B. W. and Baldwin, W. J., 1964., Provisional check list of fishes of the Revillagigedo islands., 18 pp.
|
|
|
Acknowledgements | |
I thank Ashley MacDonald and John Pickering, University of Georgia, for technical support in building this page.
|
|
| Supported by | |
|
Following modified from Australian Faunal Directory
|
Top | See original
| &pull 20q v5.145 20180528: Error 301 Moved Permanently http://biodiversity.org.au/afd/taxa/a0a0a1b0-ea9c-4b88-886c-bb6fb5eb6e6a/ |
|
Following modified from FishBase
|
Top | See original
http://www.fishbase.org/Summary/speciesSummary.php?genusname=Manta&speciesname=birostris ---> http://fishbase.de/Summary/speciesSummary.php?genusname=Manta&speciesname=birostris
http://fishbase.de/Summary/speciesSummary.php?genusname=Manta&speciesname=birostris ---> https://fishbase.de/Summary/speciesSummary.php?genusname=Manta&speciesname=birostris
https://fishbase.de/Summary/speciesSummary.php?genusname=Manta&speciesname=birostris ---> http://fishbase.de/summary/Manta-birostris.html
http://fishbase.de/summary/Manta-birostris.html ---> https://fishbase.de/summary/Manta-birostris.html
Mobula birostris, Giant manta : fisheries

You can
sponsor
this page
Common name (e.g. trout)
Genus + Species (e.g. Gadus morhua)
-

-
About this page
-
Languages
-
User feedbacks
-
Citation
-
Uploads
-
Related species
-


 Giant manta
Add your observation in
Fish Watcher
Upload your
photos
and
videos
Giant manta
Add your observation in
Fish Watcher
Upload your
photos
and
videos
Pictures
|
Videos |
Stamps, Coins Misc.
|
Google image
 Mobula birostris
Mobula birostris
Picture by
Marshall, A.
Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays) >
Myliobatiformes
(Stingrays) >
Mobulidae
(Devilrays)
Etymology: More on author:
Walbaum
.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; reef-associated; oceanodromous (Ref.
51243
); depth range 0 - 1000 m (Ref.
106604
). Subtropical; 42°N - 38°S, 180°W - 180°E (Ref.
55255
)
Circumglobal, tropical to temperate: in the Northern Hemisphere, as far north as southern California and Rhode Island on the United States west and east coasts, Mutsu Bay, Aomori, Japan, the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt and the Azores Islands; in the Southern Hemisphere, as far south as Peru, Uruguay, South Africa and New Zealand. In some locations, including Mozambique, it is sympatric with
Manta alfredi
.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: L
m
422.0
, range 380 - 460 cm
Max length : 910 cm WD male/unsexed; (Ref.
58048
); common length : 450 cm WD male/unsexed; (Ref.
3176
); max. published weight: 3.0 t (Ref.
5377
); max. reported age: 20 years (Ref.
31742
)
A giant ray having an extremely broad head with long head fins, and a terminal mouth; upper surface of disc covered with denticles, and tail usually without a spine (Ref.
5578
). Blackish above, sometimes with white shoulder patches; white below, with grey edging on disc (Ref.
5578
). Tail whiplike but short (Ref.
7251
).
Mainly in near-shore waters, near coral and rocky reefs; sometimes found over deep water (Ref.
12951
). Reported along productive coastlines with regular upwelling, oceanic island groups and offshore pinnacles and seamounts (Ref.
82755
). Penetrates shallow muddy bays and the intertidal and occurs off river mouths (Ref.
9911
). Pelagic (Ref.
58302
). Occurs singly or in loose aggregations (Ref.
12951
). Mainly plankton feeders, but may feed on small and moderate-sized fishes as well (Ref.
9911
). Leaps out the water mainly in spring and autumn, possibly as part of mating behavior (Ref.
31742
). Easily approached (Ref.
9911
). Ovoviviparous (Ref.
6902
). Commonly caught by tuna gillnet and harpoon fisheries. Utilized for its gill filter plates (very high value), meat, cartilage and skin (Ref.58048). Liver yields oil and skin used as abrasive (Ref.
6902
). World's largest ray (Ref.
37816
).
Exhibit ovoviparity (aplacental viviparity), with embryos feeding initially on yolk, then receiving additional nourishment from the mother by indirect absorption of uterine fluid enriched with mucus, fat or protein through specialised structures (Ref.
50449
). Bears up to 2 young (Ref.
5578
); born at 122-127 cm WD (Ref.58048). A female of 550 cm width and weighing 1050 kg was collected in the Galapagos in June and was carrying a well-developed embryo of 12.7 kg (Ref.
28023
). Size at partuition might be from 1.1 to 1.3 m and from 9.1 to 1.14 kg (Ref.
31742
). Yano et al (1999) (Ref.
35892
) describe the mating behavior of manta rays based on observations off Ogasawara Islands, Japan, in the following sequence: 1) 'chasing', the male rapidly follows behind the tail of the female and attacks her several times; 2) 'nipping', the male nips the tip of the pectoral fin of the female and then moves to the ventral surface of the female; 3) 'copulating', the male inserts a clasper into the cloacaof the female and copulates abdomen-to-abdomen, up to 123 seconds; 4) 'post-copulating'; 5) 'separating'. (Ref.
49562
).
Last, P.R. and J.D. Stevens
, 1994. Sharks and rays of Australia. CSIRO, Australia. 513 p. (Ref.
6871
)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref.
130435
)
Endangered (EN)
(A2bcd+3d); Date assessed:
12 November 2019
CITES
Appendix II:
International trade monitored
Appendix I & II:
Endangered migratory species conserved through agreements
Threat to humans
Harmless (Ref.
9911
)
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial
FAO - Publication:
search
|
FishSource
|
Sea Around Us
More information
Countries
FAO areas
Ecosystems
Occurrences
Introductions
Stocks
Ecology
Diet
Food items
Food consumption
Ration
Common names
Synonyms
Metabolism
Predators
Ecotoxicology
Reproduction
Maturity
Spawning
Spawning aggregation
Fecundity
Eggs
Egg development
Age/Size
Growth
Length-weight
Length-length
Length-frequencies
Morphometrics
Morphology
Larvae
Larval dynamics
Recruitment
Abundance
BRUVS
References
Aquaculture
Aquaculture profile
Strains
Genetics
Electrophoreses
Heritability
Diseases
Processing
Nutrients
Mass conversion
Collaborators
Pictures
Stamps, Coins Misc.
Sounds
Ciguatera
Speed
Swim. type
Gill area
Otoliths
Brains
Vision
Tools
Bio-Quiz
|
E-book
|
Field guide
|
Identification keys
|
Length-frequency wizard
|
Life-history tool
|
Point map
|
Classification Tree
|
Catch-MSY
|
Special reports
Check for Aquarium maintenance
|
Check for Species Fact Sheets
|
Check for Aquaculture Fact Sheets
Download XML
Summary page
|
Point data
|
Common names
|
Photos
Internet sources
AFORO (otoliths) |
Aquatic Commons
|
BHL
|
Cloffa
|
BOLDSystems
|
Websites from users
|
Check FishWatcher
|
CISTI
|
Catalog of Fishes
:
genus
,
species
|
DiscoverLife
|
DORIS
|
ECOTOX
| FAO - Publication:
search
|
Faunafri
|
Fishipedia
|
Fishtrace
| GenBank:
genome
,
nucleotide
|
GloBI
|
Google Books
|
Google Scholar
|
Google
| IGFA World Record |
MitoFish
|
National databases
|
Otolith Atlas of Taiwan Fishes
|
PubMed
|
Reef Life Survey
| Socotra Atlas |
Tree of Life
| Wikipedia:
Go
,
Search
| World Records Freshwater Fishing |
Zoological Record
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201
): 22.8 - 29, mean 27.6 °C (based on 3220 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804
): PD
50
= 0.5005 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01000 (0.00244 - 0.04107), b=3.04 (2.81 - 3.27), in cm total length, based on all LWR estimates for this body shape (Ref.
93245
).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278
): 3.5 ±0.50 se; based on food items.
Generation time: 7.3 ( na - na) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 2
growth studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179
): Very Low, minimum population doubling time more than 14 years (tm=6; tmax>20; Fec=1).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153
): High vulnerability (64 of 100).
Price category (Ref.
80766
):
Medium
.
Nutrients (Ref.
124155
): Calcium = 2.4 [0.4, 10.8] mg/100g; Iron = 0.339 [0.080, 0.946] mg/100g; Protein = 23 [18, 28] %; Omega3 = 0.1 [0.0, 0.4] g/100g; Selenium = 26.2 [7.4, 97.2] μg/100g; VitaminA = 10.6 [3.1, 37.8] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.305 [0.144, 0.613] mg/100g (wet weight);
Back to Search
Random Species
Back to Top
Accessed through:
Not available
FishBase mirror site :
localhost
Page last modified by :
mrius-barile
- 20 July 2016
Fatal error
: Uncaught ArgumentCountError: Too few arguments to function checkEcotox(), 1 passed in /var/www/html/summary/SpeciesSummary.php on line 2304 and exactly 3 expected in /var/www/html/includes/speciessummary.lib.php:2580 Stack trace: #0 /var/www/html/summary/SpeciesSummary.php(2304): checkEcotox() #1 {main} thrown in
/var/www/html/includes/speciessummary.lib.php
on line
2580
|
Updated: 2024-04-23 12:20:36 gmt
|