Classification is the way scientists divide groups of organisms into smaller closely related groups. Classifications are largely based on internal anatomy and development. To classify a new organism you must know a lot about it. To determine the classification of an organism that has already been classified is a much easier task. in order to easily identify an organisms classification, scientists often use a dichotomous key. This type of key offers the user two choices (hence the name dichotomous). By following the key you can identify the lettered turtles in the Turtle Science Box.
EXAMPLE KEY:
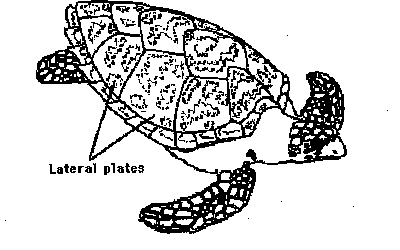
Look at the following figure of a turtle

Find out which turtle it is by using the following key. Choose which statement, la or lb that is true.
1. a Turtle's limbs are modified as flippers.........................................2
b. Turcle's limbs not modified as flippers........................................4
Look at the number to the right of the true statement. Go to that number next (if la. was true you would go to number 2 next).
2. a Shell covered with leathery skin..................................................Leatherback turtle
b. Shell coveredwith hornyplates...........................3
3. a Four lateral plates on each side of carapace...............................Atlantic Hawk's Bill Turtle
b. Five or more lateral plates on each side of carapace..................Atlantic Ridley
If you follow the key carefully you should find the correct answer, Atlantic Hawkbill. Now you are ready to try to determine the classification of the turtles in the science box. Using the Key provided, determine the classification of each lettered turtle in the Science Box. Write your answers below.
1. List different anatomical charaters of turtles that were used in the turtle key
2. On a seperate sheet of paper, explain how turtles from different classifications (families, genera, orders) are different or similar to each other. 3. Make identity cards for some of the turtles. You do not have to be an artist, just observe the turtle carefully and record information on its shape and anatomy.
1. a Limbsmodifiedasflippers............................................................................2
b. Limbs notmodified as flippers....................................................................4
2. a Shell covered with a leathery skin...........................Family Dermochelidae (leatherback turtle)
b. Shell covered with horny plates.............................Family Chelonidae (marine turtles), go to 3
3. a Width of carapace almost equal to its length; widestd part of carapace near middle of body...............................................................Atlantic ridley
b. Width of carapace obviously shorter than length; widest part of carapace near front of body.............................................................Loggerhead
4. a Plastron small and cross-shaped and does not cover most of ventral surface; tail more than half the length of carapace...FamilyChelydridae (snapping turtles)
b. Plastron large enough to cover most of ventral surface; tail less than half the length of carapace..................................................................5
a Pectoral plates of plastron not in contact with marginals..........Family Kinosternidae (mud and musk turtles), go to 6
b. Pectorals in contactwith marginals....................................................................7
6. a Pectoral plates of plastron triangular in shape.................................Genus Kinosternon ( mud turtles)
b. Pectoral plates of plastron rectangular in shape................................GenusSternotherus (musk turtles)
7. a Limbs greatly modified for digging; toes not we~bed.......................FamilyTestudinidae (land tortoises)
b. Limbs modified for swin~ming, toes webbed........................... Family Emydidae (terrapins, fresh-water turles), go to 8
8. a Plastron with hinge between pectoral and abd~minal plates, attached to carapace by ligaments; toes only slightly webbed................GenusTerrapene (boxturtles)
b. Plastron not hinged; attached directly onto carapace; toes well webbed.......................................................................9
9. a Long neck, length of neck-head region about equal to length of plastron; shell narrow, slightly elevated....................................................Chicken Turtle
b. Short neck, length of neck-head region about half the length of plastron...........................................................................................10
10. a. Posterior margin of carapace continuous, not serrated......................Genus Chrysemys (painted turtles)
b. Posterior margin of carapace serrated (edged with notched, toothlike projections) .................................................................................Genus Psedudemys
| Discover Life in Ameri ca | Education | Training Guides & Protocols | Using a Dichotomous Turtle Key |