80x5 -
240x3 -
240x4 -
320x1 -
320x2 -
320x3 -
640x1 -
640x2
Set display option above.
Click on
images to enlarge. |

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus porosus |
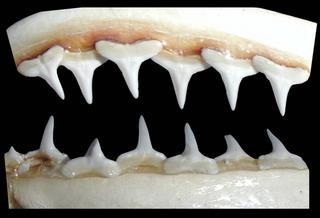
© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus limbatus |
|
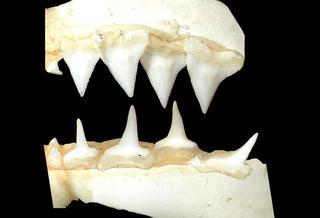
© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus plumbeus |
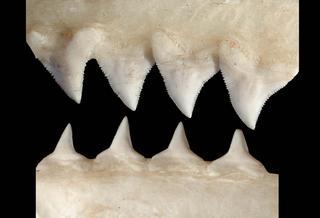
© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus obscurus |
|
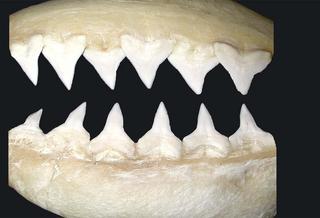
© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus leucas |
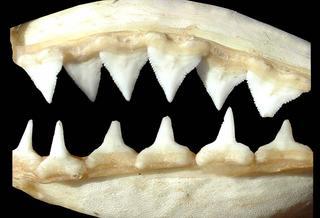
© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus galapagensis |
|

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus brachyurus |

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus altimus |
|

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Carcharhinus longimanus |

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Rhizoprionodon longurio |
|

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Rhizoprionodon |
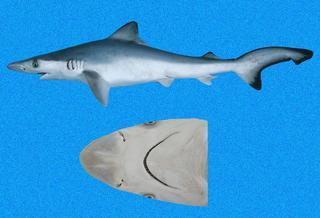
© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Rhizoprionodon longurio |
|

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Negaprion brevirostris |
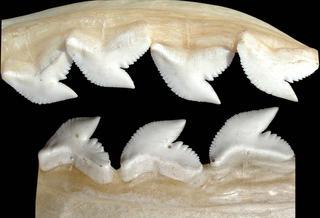
© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Galeocerdo cuvier |
|

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Triaenodon obesus |

© Copyright Ross Robertson, 2006
· 12
Triaenodon obesus |
|

© Copyright Lucy Beeching 2010
· 1
Glyphis cicatricosa |

© Copyright Lucy Beeching 2010
· 1
Glyphis cicatricosa |
|

© Copyright Photographer/SFTEP, 2002
· 0
Carcharhinus albimarginatus |

© Copyright Doug Perrine, 2006
· 0
Carcharhinidae |
See
| | |
| | IDnature guides | |
| Overview |
Main identification features
- 1st dorsal fin before pelvic
- upper tail fin lobe - undulating ridge
- snout overhanging
- gill slits: 5, 1-2 over pectoral
- c: asymmetric, lower lobe well defined
FAMILY CARCHARHINIDAE
REQUIEM SHARKS, BLUE SHARKS, LEMON SHARKS, SHARPNOSE SHARKS, TIGER SHARKS, WHITENOSE SHARKS, WHITETIP SHARKS
The requiems are one of the largest and best known family of sharks. Worldwide there are 50 species in 12 genera; 17 species in 7 genera occur in our region. They are active strong swimmers that occur singly or in small to large groups. They span a considerable range of sizes. For example, some milk sharks (genus Rhizoprionodon) reach a maximum length of less than 100cm, whereas the Tiger Shark (Galeocerdo cuvier) is among the largest of sharks with a maximum size of at least 7.4 m. Except for the Tiger Shark, which is ovoviviparous, all species are viviparous with a yolk sac placenta. They have litters of young that number from one or two to as many as 135. The pups resemble miniature versions of the adults and are able to fend for themselves moments after birth. Requiem sharks are responsible for about half of all reported shark attacks on humans. However, less than 100 attacks are reported each year worldwide and no more than 30 of these are fatal. Although attacks are extremely rare, the potential danger of the more aggressive species, such as the Tiger and Bull sharks, should be recognized. Spearfishermen are more prone to shark attack than other divers because fishes struggling on a spear emit low frequency vibrations which can attract sharks unerringly to the site. Once in the vicinity, the presence of blood, which is readily detected by the keen olfactory sense, adds to these sharks aggressive behavior. A few species have been shown to exhibit threat posturing involving exaggerated lateral swimming movements (i.e. arc of movement of the head increases noticeably), arching the back, holding the pectoral fins downward, and snapping of jaws. If these motions are evident, one should move slowly away from the shark and exit the water. They are voracious predators that feed mainly on a variety of fishes, other sharks, rays, squid, octopuses, cuttlefish, crabs, lobsters, and shrimps. Lesser items include sea birds, turtles, sea snakes, marine mammals, molluscs, and carrion, as well as human garbage.
Requiem sharks are characterized by having eyes with internal nictitating membranes; grooves along the side of the lips; teeth of variable sizes, with or without accessory points, upper and bottom teeth have different forms; 1st dorsal fin smaller than upper lobe of tail, situated before the pelvic fins; 2nd dorsal much smaller than 1st; lower lobe of tail well developed, upper lobe with undulating ridge along its top edge.
|
| References |
- Acero, A. and Franke, R., 2001., Peces del parque nacional natural Gorgona. En: Barrios, L. M. y M. Lopéz-Victoria (Eds.). Gorgona marina: Contribución al conocimiento de una isla única., INVEMAR, Serie Publicaciones Especiales No. 7:123-131.
- Allen , G.R. and Robertson, D.R., 1997., An Annotated Checklist of the fishes of Clipperton Atoll, Tropical Eastern Pacific., Revista de Biologia Tropical, 45:813-843.
- Balart , E. F. , Castro-Aguirre , J. L. , Aurioles-Gamboa , D. , García-Rodriguez , F. and Villavicencio-Garayzar, C., 1995., Adiciones a la ictiofauna de Bahía de la Paz, Baja California Sur, México., Hidrobiologica, 5:79-85.
- Bellido-Millán, J.M. and Villavicencio-Garayzar, C.J., 2002., Pesqueria artesanal de tiburon en la region central del Golfo de California. En: Lozano-Vilano, M. L. (Ed.). Libro Jubilar en Honor al Dr. Salvador Contreras Balderas., Universidad Autonoma de Nuevo León:143-152.
- Breder, C.M. Jr., 1928., Scientific results of the second oceanographic expedition of the "Pawnee" 1926. Elasmobranchii from Panama to Lower California., Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Collect. Yale Univ., 2(1):1-13.
- Béarez, P., 1996., Lista de los Peces Marinos del Ecuador Continental., Revista de Biologia Tropical, 44:731-741.
- Candanedo , C. and D'Croz, L., 1983., Ecosistema acuático del lago Bayano: un embalse tropical., Publicación Técnica IRHE, Dirección de Ingenieria, Departamento de Hidrometeorología, Panamá., :38pp.
- Castri-Aguirre, J.L., Espinoza-Pérez, H. and Schmitter-Soto, J.J., 2002., Lista sitemática, biogeográfica y ecológica de la ictiofauna estuarino lagunar y vicaria de México. En: Lozano-Vilano, M. L. (Ed.). Libro Jubilar en Honor al Dr. Salvador Contreras Balderas., Universidad Autonoma de Nuevo León:117-142.
- Castro-Aguirre, J.L. and Balart, E.F., 2002., La ictiofauna de las islas Revillagigedos y sus relaciones zoogeograficas, con comentarios acerca de su origen y evolucion. En: Lozano-Vilano, M. L. (Ed.). Libro Jubilar en Honor al Dr. Salvador Contreras Balderas., Universidad Autonoma de Nuevo León:153-170.
- Castro-Aguirre, J.L., 1999., Ictiofauna estuarino-lagunar y vicaria de México., Editorial Limusa S.A. de C.V.: 1-629pp.
- Compagno , L. J. V. and Cook, S. F., 1995., The exploitation and conservation of freshwater elasmobranchs: status of taxa and prospects for the future., Journal of Aquariculture and Aquatic Sciences, 7:62-90.
- Compagno, L.J.V., 1999., Checklist of living elasmobranchs. In Hamlett W.C. (ed.) Sharks, skates, and rays: the biology of elasmobranch fishes., The John Hopkins University Press:471-498.
- Compagno, L.J.V., 1984., Sharks of the World. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date. Part 2. Carcharhiniformes. FAO Species Catalogue., FAO Fish. Synop. No 125, 4(2):251-655.
- Cuesta, T.C., 1932., Lista de los peces de las costas de la Baja California., Inst. Biol. Mexico, Anal, 3(1):75-80.
- Edgar, G.J. Banks, S., Fariña, J.M., Calvopiña, M. and Martínez, C., 2004., Regional biogeography of shallow reef fish and macro-invertebrate communities in the Galapagos archipelago., Journal of Biogeography, 31:1107-1124.
- Eschmeyer , W. N. , Herald , E. S. and Hamman, H., 1983., A field guide to Pacific coast fishes of North America from the Gulf of Alaska to Baja California. Peterson Field Guide Ser. 28., Houghton Mifflin:336pp.
- Findley, L.T., Hendrickx, M.E., Brusca, R.C., van der Heiden, A.M., Hastings, P.A., Torre, J., 2003., Diversidad de la Macrofauna Marina del Golfo de California, Mexico., CD-ROM versión 1.0. Projecto de la Macrofauna del Golfo . Derechos reservados de los autores y Conservación Internacional.
- Fischer , W. , Krup , F. , Schneider , W. , Sommer , C. , Carpenter , K. E. and Niem, V. H., 1995., Guia FAO para la Identificacion de Especies de para los fines de la Pesca. Pacifico Centro-Oriental. Volumen II. Vertebrados - Parte 1., FAO2:647-1200.
- Fowler, H.W., 1944., Results of the Fifth George Vanderbilt Expedition (1941) (Bahamas, Caribbean sea, Panama, Galapagos Archipelago and Mexican Pacific Islands). The Fishes., Acad. Nat. Sci. Philadel., Monographs, 6:57-529.
- Galván-Magaña, F., Abitia-Cárdenas, L.A., Rodríguez-Romero, J., Pérez-España, H., Chávez-Ramos, H., 1996., Systematics list of the fishes from Cerralvo island, Baja California Sur, Mexico., Ciencias Marinas, 22:295-311.
- Galván-Magaña, F., Gutiérrez-Sánchez, F., Abitia-Cárdenas, L.A., Rodríguez-Romero, J., 2000., The distribution and affinities of the shore fishes of the Baja California Sur lagoons. In Aquatic Ecosystems of Mexico: Status and Scope. Eds. M. Manuwar, S.G. Lawrence, I.F. Manuwar & D.F. Malley. Ecovision World Monograph Series., Backhuys Publishers:383-398.
- Gelsleichter , J. , Musick , J. A. and Nichols, S., 1999., Food habits of the smooth dogfish, Mustelus canis, dusky shark, Carcharhinus obscurus, Atlantic sharpnose shark, Rhizoprionodon terraenovae, and the sand tiger, Carcharias tauruss, from the northwest Atlantic Ocean., Environmental Biology of Fishes, 54:205-217.
- Gotshall, D.W., 1996., Fishes of Rocas Alijos. In Rocas Alijos. Ed. R. W. Schmieder. Cornell Expeditions., Kluwer Academic Publishers: 347-354.
- Günther, A., 1870., Catalogue of the fishes in the British Museum. Catalogue of the Physostomi, containing the families Gymnotidae, Symbranchidae, Muraenidae, Pegasidae, and of the Lophobranchii, Plectognathi, Dipnoi, ...[thru] ... Leptocardii, in the British Museum., Brithish Museum (Natural History)8:1-549.
- Hildebrand, S.F., 1946., A descriptive catalog of the shore fishes of Peru., Bull. U.S. Nat. Mus., 189:1-530.
- Humann, P., 1993., Reef Fish Identification: Galapagos., New World Publishing:192pp.
- Jimenez-Prado, P., Béarez, P., 2004., Peces marinos del Ecuador continental / Marine fishes of continental Ecuador., SIMBIOE/NAZCA/IFEA tomo 1 y 2.
- Jordan , D.S. and Bollman, C.H., 1890., Descriptions of new species of fishes collected at the Galapagos Islands and along the coast of the United States of Colombia, 1887-88, by the U.S. Fish Commission steamer 'Albatross'., Proc. U.S. Nat. Mus., 12:149-183.
- Jordan , D.S. and Evermann, B.W., 1898., The fishes of North and Middle America: a descriptive catalogue of the species of fish-like vertebrates found in the waters of North America, north of the Isthmus of Panama. Part III., Bull. U.S. Nat. Mus., 47:2183-3136.
- Jordan , D.S. and Gilbert, C.H., 1882., Description of four new species of sharks, from Mazatlan, Mexico., Proc. U.S. Nat. Mus., 5:102-110.
- Jordan , and McGregor,., 1898., List of fishes collected at the Revillagigedo archipelago and neighboring islands., Rept. U.S. Fisheries Comm., 24:271-284.
- Jordan, D.S., 1895., The fishes of Sinaloa., Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences (Series 2), 5:377-514.
- Lea, R.N. and Rosenblatt, R.H., 2000., Observations on fishes associated with the 1997-1998 El Niño off California., CalCOFL Rep., 41:117-129.
- Lesueur, C. A., 1818., Description of several new species of North American fishes., J. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila., 1:222-235.
- Lesueur, C. A., 1822., Description of a Squalus, of a very large size, which was taken on the coast of New-Jersey., J. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila., 2:343-352.
- Linnaeus, C., 1758., Systema Naturae, Ed. X. (Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata.) Holmiae., Systema Nat. ed. 10, 1:1-824.
- Lopez , M. I. and Bussing, W. A., 1982., Lista provisional de los peces marinos de la Costa Rica., Revista de Biologia Tropical, 30(1):5-26.
- Love, M.S., Mecklenburg, C.W., Mecklenburg, T.A., Thorsteinson, L.K., 2005., es of the West Coast and Alaska: a checklist of North Pacific and Artic Ocena species from Baja California to the Alaska-Yukon border., U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, Biological Resources Division, 288pp.
- Madrid Vera , J. , Ruíz Luna , A. and Rosado Bravo, I., 1998., Peces de la plataforma continental de Michoacán y sus relaciones regionales en el Pacífico mexicano., Revista de Biologia Tropical, 42(2):267-276.
- McCosker , J.E. and Rosenblatt, R.H., 1975., Fishes collected at Malpelo Island. In Graham, J.B. (ed.) The Biological Investigation of Malpelo Island, Colombia., Smithsonian Contrib. Zool., 176:91-93.
- Meek , S.E. and Hildebrand, S.F., 1923., The marine fishes of Panama. Part I., Field Mus. Nat. Hist., Zool. Ser. Publ., XV:1-330.
- Minckley, W.L., 2002., Fishes of the lowermost colorado river, its delta, and estuary: a commentary on biotic change. En: Lozano-Vilano, M. L. (Ed.). Libro Jubilar en Honor al Dr. Salvador Contreras Balderas., Universidad Autonoma de Nuevo León:63-78.
- Musick, J.A., Harbin, M.M., Berkeley, S.A., Burgess, G.H. Eklund, A.M., Findley, L., Gilmore, R.G., Golden, J.T., Ha, D.S., Huntsman, G.R., McGovern, J.C., Parker, S.J., Poss, S.G., Sala, E., & Schmidt, T.W., Sedberry, G.R., Weeks, H., Wright, S.G., 2000., Marine, estuarine, and diadromous fish stocks at risk of extinction in North America (exclusive of Pacific salmonids)., Fisheries, 25:6-30.
- Müller , J. and Henle, F. G. J., 1839., Systematische Beschreibung der Plagiostomen. Berlin., Plagiostomen, :27-102.
- Nardo,., 1827., Prodromus observationum et disquisitionum Adriaticae ichthyologiae., Giorn. Fisica Chimica Storia Nat. Med. Arti, Pavia, 10:22-40.
- Nelson, J.S., 1984., Fishes of the World (Third edition)., John Wiley and Sons:523pp.
- Orellana, J.J., 1985., Marine Fishes of Los Cóbanos: Fishes of El Salvador., Sigma Found:126pp.
- Osburn , R. C. and Nichols, J. T., 1916., Shore Fishes Collected by the 'Albatross' Expedition in Lower California with Descriptions of New Species., Bull. Amer. Mus. Nat. Hist., 35:139-181.
- Phillips, P. C., 1981., Annotated Checklist of Fishes at Jiquilisco Bay, El Salvador., Revista de Biologia Tropical, 29:45-58.
- Poey, F., 1860., Memorias sobra la historia natural de la Isla de Cuba, acompañadas de sumarios Latinos y extractos en Francés. Tomo 2. La Habana., Mem. Hist. Nat. Cuba, 2:97-336.
- Poey, F., 1868., Synopsis piscium cubensium. Catalogo Razonado de los peces de la isla de Cuba., Repertorio Fisico-Natural de la Isla de Cuba, 2:279-484.
- Ramírez Rodríguez, M., 1997., Producción pesquera en la Bahía de La Paz, B.C.S.. En Urbán Ramírez, J. y M. Ramírez Rodríguez (Eds.). La Bahía de La Paz investigación y conservación., Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur:273-282.
- Ranzani,., 1840., De novis speciebus piscium. Dissertatio prima., Novi Comment. Acad. Sci. Inst. Bonon., 4:65-83.
- Ricker, K.E., 1959., Fishes collected from the Revillagigedo Islands during the 1954-1958 cruises of the "Marijean."., Univ. Brit. Columbia Inst. Fish., Mus. Contrib., 4:10pp.
- Ricker, K.E., 1959., Mexican shore and pelagic fishes collected from Acapulco to Cape San Lucas during the 1957 cruise of the "Marijean"., Univ. Brit. Columbia Inst. Fish., Mus. Contrib., 3:18pp.
- Robertson , D.R. and Allen, G.A., 1996., Zoogeography of the shorefish fauna of Clipperton Atoll., Coral Reefs, 15:121-131.
- Rosenblatt , R.H. , McCosker , J.E. and Rubinoff, I., 1972., Indo-west Pacific fishes from the Gulf of Chiriqui, Panama., Contrib. Sci. Nat. Hist. Mus. Los Angeles Co., 234:18pp.
- Rubio , R. E. A. and Estupiñan, F., 1990., Ictiofauna del Parque Nacional Natural Sanquianga, un Analisis de su Estructura y Perspectivas para su Manejo., Memorias del VII Seminario Nacional de las Ciencias y Tecnologías del Mar. Comisión Colombiana de Oceanografía. Bogota, Colombia., :660-670.
- Rubio, E.A., 1986., Notas sobre la ictiofauna de la Isla de Gorgona, Colombia., Boletin Ecotropica. Univ. Bog. Jorge Tadeo Lozano, 13:86-112.
- Rubio, E.A., 1988., Estudio taxonomico de la ictiofauna acompañante del camaron en areas costeras del Pacifico de Colombia., Memorias del VI Seminario Nacional de las Ciencias del Mar. Comisión Colombiana de Oceanografía. Bogota, Colombia., :169-183.
- Rüppell, W. P. E. S., 1837., Neue Wirbelthiere zu der Fauna von Abyssinien gehörig., Fische des Rothen Meeres, 1837:53-80.
- Snodgrass , R. E. and Heller, E., 1905., Papers from the Hopkins Stanford Galapagos expedition, 1898-1899. XVII. Shorefishes of the Revillagigedo, Clipperton, Cocos and Galapagos Island., Proc. Wash. Acad. Sci., 6:333-427.
- Springer, S., 1950., A revision of North American sharks allied to the genus Carcharhinus., Amer. Mus. Novit., (1451):1-13.
- Starks, E. C., 1906., On a Collection of fishes made by P. O. Simons in Ecuador and Peru., Proc. U.S. Nat. Mus., 30:761-800.
- Van der Heiden , A. M. and Findley, L. T., 1988., Lista de los peces marinos del sur de Sinaloa, México., Anales del Centro de Ciencias del Mar y Limnologia de la Universidad Autonoma Nacional de Mexico, 15:209-224.
- Vega, A.J., Villareal, N., 2003., Peces asociados a arrecifes y manglares en el Parque Nacional Coiba., Tecnociencia, 5:65-76.
- Villareal-Cavazos, A., Reyes-Bonilla, H., Bermúdez-Almada, B. and Arizpe-Covarrubias, O., 2000., Los peces del arrecife de Cabo Pulmo, Golfo de California, México: Lista sistemática y aspectos de abundancia y biogeografía., Rev. Biol. Trop., 48:413-424.
- Villavicencio Garayzar , C. J. , Mariano Meléndez , E. and Downton Hoffmann, C., 1997., Tiburones capturados comercialmente en la Bahía de La Paz, B.C.S.. En Urbán Ramírez, J. y M. Ramírez Rodríguez (Eds.). La Bahía de La Paz investigación y conservación., Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur:201-236.
- Walker, B. W. and Baldwin, W. J., 1964., Provisional check list of fishes of the Revillagigedo islands., 18 pp.
|
| Acknowledgements | |
I thank Ashley MacDonald and John Pickering, University of Georgia, for technical support in building this page.
|
Top
Updated: 2024-11-10 19:41:09 gmt
© Designed by The Polistes Corporation
|
|